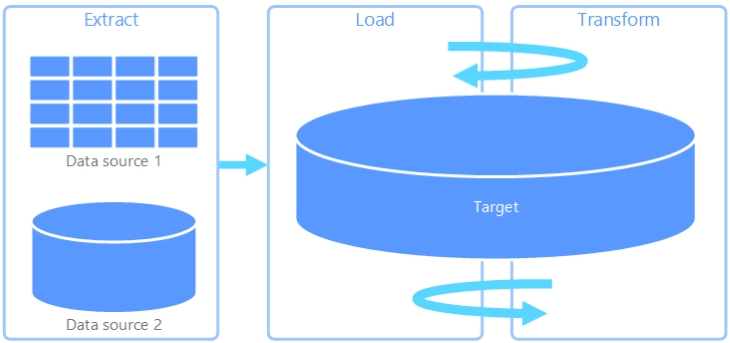
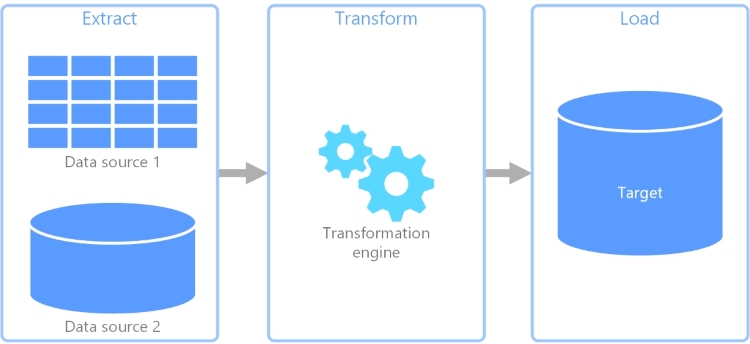
ETL is often favored when data requires significant transformations, strict data governance and structured processing. ELT is suitable for scenarios involving large volumes of data, flexible analysis and leveraging the processing power of modern platforms.
ETL benefits and drawbacks
While ETL and ELT offer many benefits to data users, they also have some drawbacks.
Benefits
- Compliance: When it comes to security, ETL is more secure compared to ELT. ETL architecture is designed to comply with various industry standards, including GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA. This helps data teams protect sensitive information before loading it into the target system.
- Maturity: ETL history can be traced back to the 70s era. Many data engineers are familiar with its architecture and how to use it. ETL also has an extensive documentation library, making learning accessible for novices.
- Ideal for complex projects: ETL is appropriate for processing structured data that requires complex transformation.
Drawbacks
- Expensive to maintain: ETL can be cost-intensive due to the ongoing cost of maintaining a data transformation server. ETL often requires significant computing power and resources in the intermediary staging area for performing complex transformations.
- Limited flexibility: Data engineers must define the data source early and transform it before loading it into the target system.
ELT benefits and drawbacks
Benefits
- Quicker loading: ELT architecture supports both structured and unstructured data, meaning data from sources can be loaded into the data warehouse without going through any transformation process.
- Real-time, flexible data analysis: ELT allows for loading raw data into the target system, providing flexibility to perform transformations on demand based on specific use cases or analytic requirements.
- Low maintenance: ELT is cloud-based; it requires no specialized hardware, making it easy to manage and maintain. ELT also leverages the processing power and scalability of modern data platforms or cloud-based systems.
Drawbacks
- Data governance and quality concerns: ELT accepts all kinds of data from sources, exposing sensitive data. It doesn’t comply with GDPR, HIPAA or CCPA standards.
- Dependency on target system capabilities: ELT heavily relies on the processing power and capabilities of the target system. In some cases, the target system may need to provide robust transformation functionalities, limiting the flexibility of the approach.